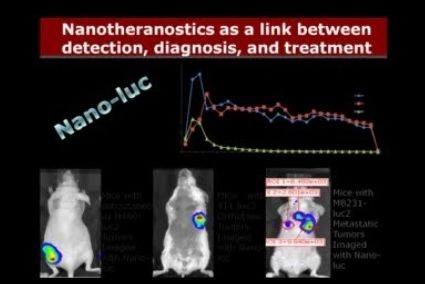
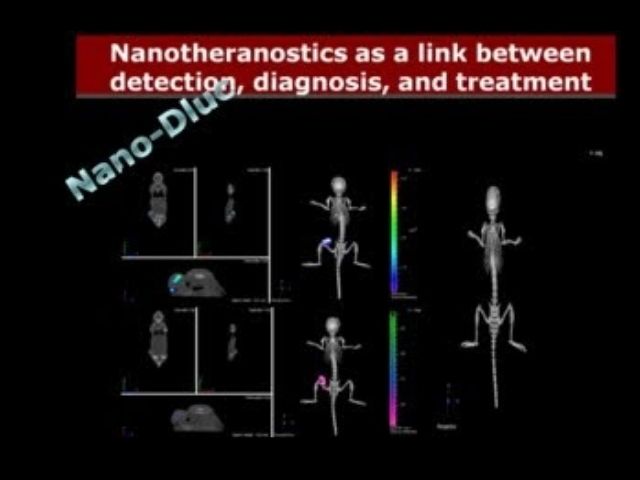
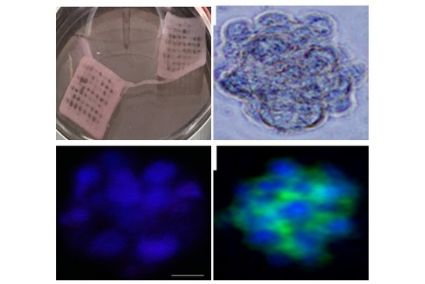
One important part of our research is to enhance the delivery of liposomes to tumors cells by overcoming stromal barriers by using drugs like Telmisartan and Losartan, and withaferin. Apart from this, our research group is also delivering siRNA to tumor cells by using liposomal delivery systems. Imaging of targeted liposomes is also done using various chemoluminescence and bioluminescence markers.
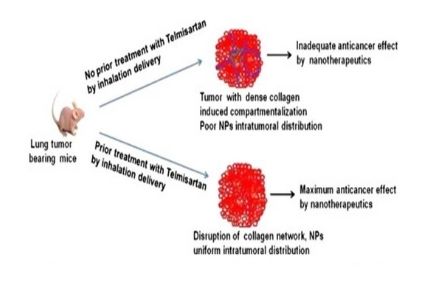
Schematic representation of inhalation use of TEL to reduce tumor fibrosis and increase nanoparticle intratumoral distribution.
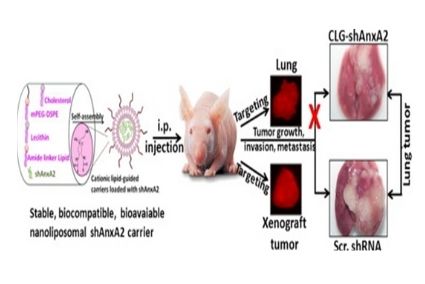
Cationic lipid guided short-hairpin RNA interference of annexin A2 attenuates tumor growth and metastasis in a mouse lung cancer stem cell model.
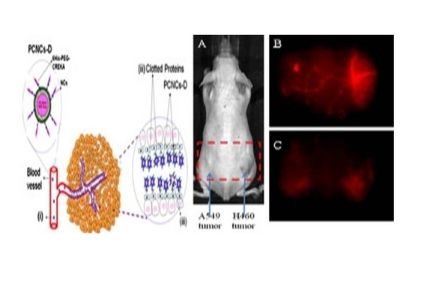
Theranostic tumor homing nanocarriers for the treatment of lung cancer: Nanoparticles conjugated with 6His-PEG2000-CREKA through DOGS-Ni-NTA for targeting tumor vasculature (PCNCs-D)
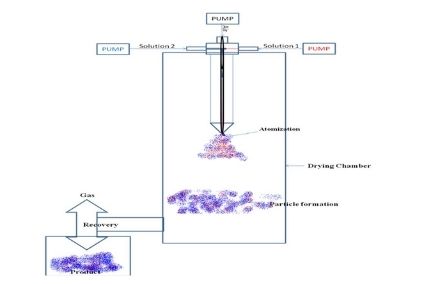
Schematic diagram of the dual-channel spray drying system. Effect of Drug XX on angiogenesis by Tube formation assay.
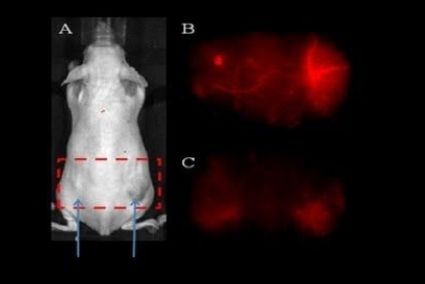
In-Vivo Imaging. (A) A549 and H460 lung cancer cell tumor-bering mouse in in-vivo imaging system and Spectrally Unmixed Image of Vasculature with, (B) PCNCs-Di targeting vasculature and (C) NCs-Di.
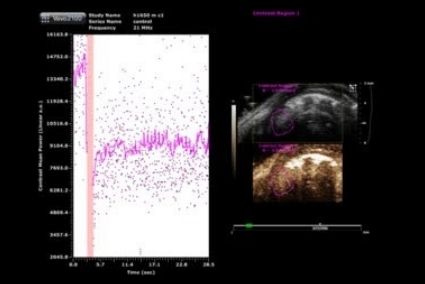
Micro-ultrasound is a real-time modality, molecular imaging, and quantification of angiogenesis using the microbubbles conjugated to ligands targeting VEGFR2 Control tumor-bearing mice.




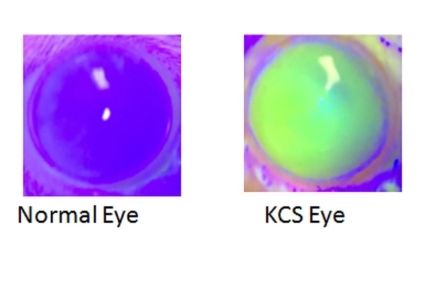
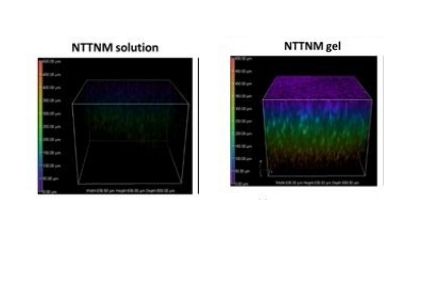 Corneal penetration study in swine eyeballs. Fluorescence with color-coding of depth
(z in μm)
Corneal penetration study in swine eyeballs. Fluorescence with color-coding of depth
(z in μm)




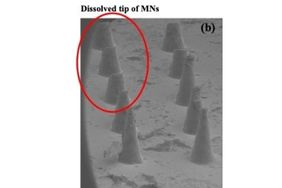

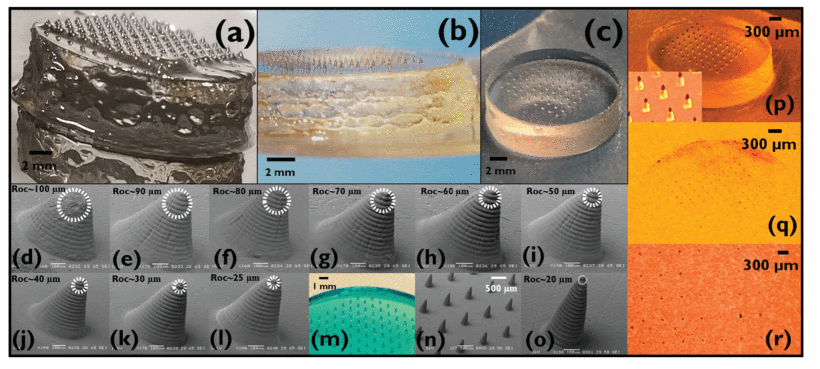 "(a): “Partially Polymerized Membrane” effect on the base on the iμ NA due to background printing from over-exposure, which peels off as the polymer matrix
is not completely polymerized in the portions of the structure between the μN bases. (b) “Pancaking” effect on the edges of the iμ NA base. (c) Optimally printed iμ NA. (d-l) Optimization of the aspect ratio (AR) of the iμ NA to successfully achieve the desired ROC to penetrate human skin. (m) iμ NA dyed in methylene blue shows that the polymer matrix retains its hydrogel properties
post-printing, allowing for “intelligent” release. (n) SEM image of an optimal aspect
ratio iμ NA having a ROC of ∼20 μm (o). (p) Dyeing the tips with Gentian Violet to study the effect of penetration
on an artificial skin model. (q) Photomicrographs showing successful penetration of
an entire 10×10 array with a close-up image in (r)." Kundu et al. (2020)
"(a): “Partially Polymerized Membrane” effect on the base on the iμ NA due to background printing from over-exposure, which peels off as the polymer matrix
is not completely polymerized in the portions of the structure between the μN bases. (b) “Pancaking” effect on the edges of the iμ NA base. (c) Optimally printed iμ NA. (d-l) Optimization of the aspect ratio (AR) of the iμ NA to successfully achieve the desired ROC to penetrate human skin. (m) iμ NA dyed in methylene blue shows that the polymer matrix retains its hydrogel properties
post-printing, allowing for “intelligent” release. (n) SEM image of an optimal aspect
ratio iμ NA having a ROC of ∼20 μm (o). (p) Dyeing the tips with Gentian Violet to study the effect of penetration
on an artificial skin model. (q) Photomicrographs showing successful penetration of
an entire 10×10 array with a close-up image in (r)." Kundu et al. (2020)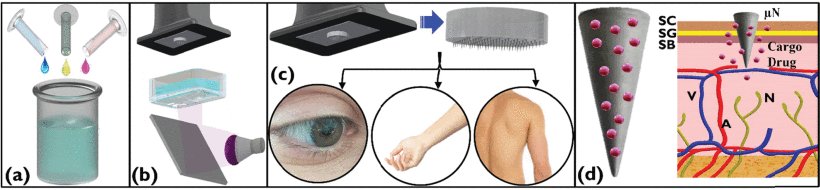 "(a): Schematic of PEGDA (blue) being mixed with 2.5 wt% Diphenyl (2, 4, 6-trimethylbenzoyl)
phosphine oxide (TPO) (green) and 0.25wt% therapeutic cargo of diclofenac sodium (pink).
(b) DLP 3D printing of the prepared polymer matrix with a UV light source of 385 nm
onto the build platform. The iμNA printed consists of a sacrificial base plate and
a raft to improve the adhesion of the 3D printed device onto the build platform. (c)
Removal of the iμNA from the build platform to have the final iμNA, which may be used
for ocular, acute, and chronic drug delivery via transdermal route and allergen testing
on the human torso, among other applications. (d) Close-up of a singular API loaded
μNA in the intelligent polymer matrix showing the stimulus-based release of the drugs
upon sensing its external environment change while retaining the non-drug PEGDA matrix."
Kundu et al. (2020)
"(a): Schematic of PEGDA (blue) being mixed with 2.5 wt% Diphenyl (2, 4, 6-trimethylbenzoyl)
phosphine oxide (TPO) (green) and 0.25wt% therapeutic cargo of diclofenac sodium (pink).
(b) DLP 3D printing of the prepared polymer matrix with a UV light source of 385 nm
onto the build platform. The iμNA printed consists of a sacrificial base plate and
a raft to improve the adhesion of the 3D printed device onto the build platform. (c)
Removal of the iμNA from the build platform to have the final iμNA, which may be used
for ocular, acute, and chronic drug delivery via transdermal route and allergen testing
on the human torso, among other applications. (d) Close-up of a singular API loaded
μNA in the intelligent polymer matrix showing the stimulus-based release of the drugs
upon sensing its external environment change while retaining the non-drug PEGDA matrix."
Kundu et al. (2020)